Production
Curbing Global Warming
Energy is necessary for the production of vehicles and CO2 is generated by the consumption of energy. In recent years, Nissan Shatai has endeavored to curb global warming by working to improve its operational and management methods.
FY2024 Achievements
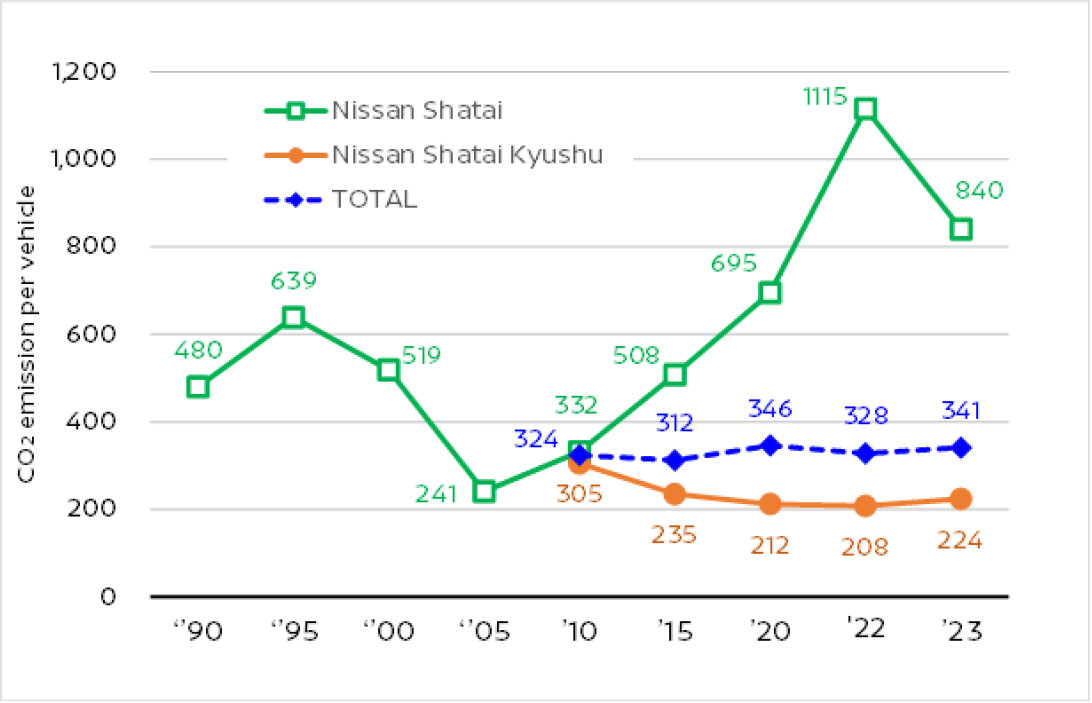
Trends in CO2 emissions per production vehicle

3WET painting greatly reduces CO2
In the painting of vehicles there is a process involving bake-drying the paint at a high temperature, and the CO2 emissions from the painting plant constitute approximately one quarter of the emissions of the entire plant. Nissan Shatai Kyushu has adopted 3WET which eliminates the bake-drying after the application of the middle coat in order to reduce CO2 emissions.
Moreover, in response to the increase in CO2 due to the water-based topcoat color base paint we adopted to reduce VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds) (drying equipment for evaporating the moisture is necessary), we have adopted the “Air Shield Integrated with a Painting Machine ” which integrates drying equipment with the paint gun (jointly developed with Taikisha Ltd. ), cutting in half the moisture evaporation time. Due to this, we have reduced the CO2 emissions from the topcoat color base to the clear paint by 25% (the highest level in the world).
Due to these measures, we have reduced CO2 emissions in the painting plant overall by 16%.
Content of the main initiatives in FY2024
Improvement of energy-saving at the production plant facilities
In FY2024, we are continuing to replace conventional lighting with LEDs and have started introducing clean energy, and we will continue our efforts towards stable production activities (improvement of operation rates and direct run rates),thereby advancing activities to curb global warming.
The Progress of the Initiatives
| FY2003 | Adoption of a building cooling system which uses photocatalysts |
|---|---|
| FY2004 | Construction of an energy monitoring system |
| Implementation of the downsizing of the boilers in Zone 1 | |
| Construction of an improvement system for compressor control | |
| Installation of freon recovery equipment | |
| FY2005 | Installation of a co-generation system in the Techno Center <Gas engine> Water-cooled 4 cycle, V20 cylinder, 48,700cc <Amount of electricity generated> 920KW <Use of exhaust heat> Used in refrigeration using an absorption refrigerating machine Used in feed-water heating of the boiler <Effect> Reduction of CO2 emissions: down 650 tons/year |
| Implementation of the downsizing of the boilers in the Techno Center | |
| FY2006 | Adoption of energy-saving lamps |
| Management of truck transportation | |
| FY2007 | Stopping of the A color topcoat painting production line in Zone 1 |
| FY2010 | Commencement of production at Nissan Shatai Kyushu |
| Consolidation of production of the three vehicle models produced in Zone 1 into Zone 2 | |
| FY2011 | Implementation of special summertime power saving activities (July to September) (night shift for operating times, changes to holidays, etc.) |
| Stopping of the Zone 1 painting plant due to the consolidation of the painting process | |
| FY2013 | All of the buildings and facilities in the areas subject to closure in Zone 1 are consolidated into other zones |
| FY2014 | Nissan Shatai: Inverterization of the paint electrodeposition circulation pump Nissan Shatai Kyushu: Adoption of the microfine particle painting method |
| FY2015 | Nissan Shatai: Improvement of production efficiency by converting the resin plant into a single production line |
| FY2016 | Nissan Shatai: Conversion of the welfare building fluorescent lights and mercury lights into LEDs Nissan Shatai Kyushu: Conversion of the lighting into LEDs |
| FY2017 | Nissan Shatai: Reduction of the temperature in the resin painting ovens |
| FY2018 | Nissan Shatai: Renewal of the Techno Center refrigerating machines |
| FY2019 | Conversion of the Techno Center Main Design Building fluorescent lights into LEDs |
| FY2020 | Conversion of the Hadano Experiment Department office building fluorescent lights into LEDs |
| FY2021 | Conversion of some of the Techno Center Processing Machines Administration Building fluorescent lights into LEDs Conversion of the Hadano Experiment Department workspace fluorescent lights into LEDs |
| FY2022 | Nissan Shatai: Energy saving through the use of small air compressers at the sheet metal plant of the press factory Nissan Shatai Kyushu: Energy saving by improving electrodeposited chiller function |
| FY2023 | Promotion of the conversion of lighting to LEDs at Nissan Shatai and Nissan Shatai Kyushu |
| FY2024 | Introducing clean energy |
Reduction of waste
We are working to encourage recycling of the waste generated in the vehicle production process. Furthermore, we tackle activities to reduce the amount of waste, and advance activities in accordance with our Plan on the Reduction of Generation of By-products, etc. based on the Act on the Promotion of Effective Utilization of Resources, to maintain our recycling rate at 100%.
FY2024 Achievements
Reduction of the amount of waste generated
Results in FY2024| Target | Achievement | |
|---|---|---|
| Nissan Shatai Co., Ltd. | 481 tons or less | 468 tons |
| Nissan Shatai Kyushu Co. Ltd. | 2,818 tons or less | 2,965 tons* |
* Partial treatment of effluent as industrial waste due to water treatment facility construction.
The Progress of the Initiatives
| FY2012 | Nissan Shatai Kyushu: Reduction of the amount of sludge generated through reduction of the water content ratio of paint sludge (paint sludge reduced 50%) |
|---|---|
| FY2013 | Reduction of the amount of waste generated through upgrades of the glass sealing supply facilities (40% reduction in the amount of waste in one drum) |
| FY2014 | Nissan Shatai: Reduction of the amount of sludge generated through reduction of the water content ratio of paint sludge (adoption of the Nissan Shatai Kyushu items) |
| FY2016 | Nissan Shatai: Techno Center and the Hadano Plant Cost reduction and waste reduction by changing from bumper waste treatment to valuable sales |
| FY2017 | Nissan Shatai: Proper storage of cardboard (prevention of cardboard becoming industrial waste due to wetness from rain) |
| FY2019 | Prevention of scattering due to Styrofoam being converted into microplastics when it is collected Extraction of valuable purchased goods due to changes to the waste plastic sorting method |
| FY2020 | Nissan Shatai: Creating value through engine hanger sorting and collection Nissan Shatai: Expansion of resources recycling by strengthening sorting through the development of waste storage places |
| FY2022 | Nissan Shatai: Expansion in the creation of value due to separate collection of iron and aluminum |
| FY2023 | We improved our waste treatment overfenders to make them valuable |
| FY2024 | Nissan Shatai: Adoption of high-pressure washing machines for slatted floor cleaning to reduce chemical waste |
FY2024 Waste Treatment Procedure
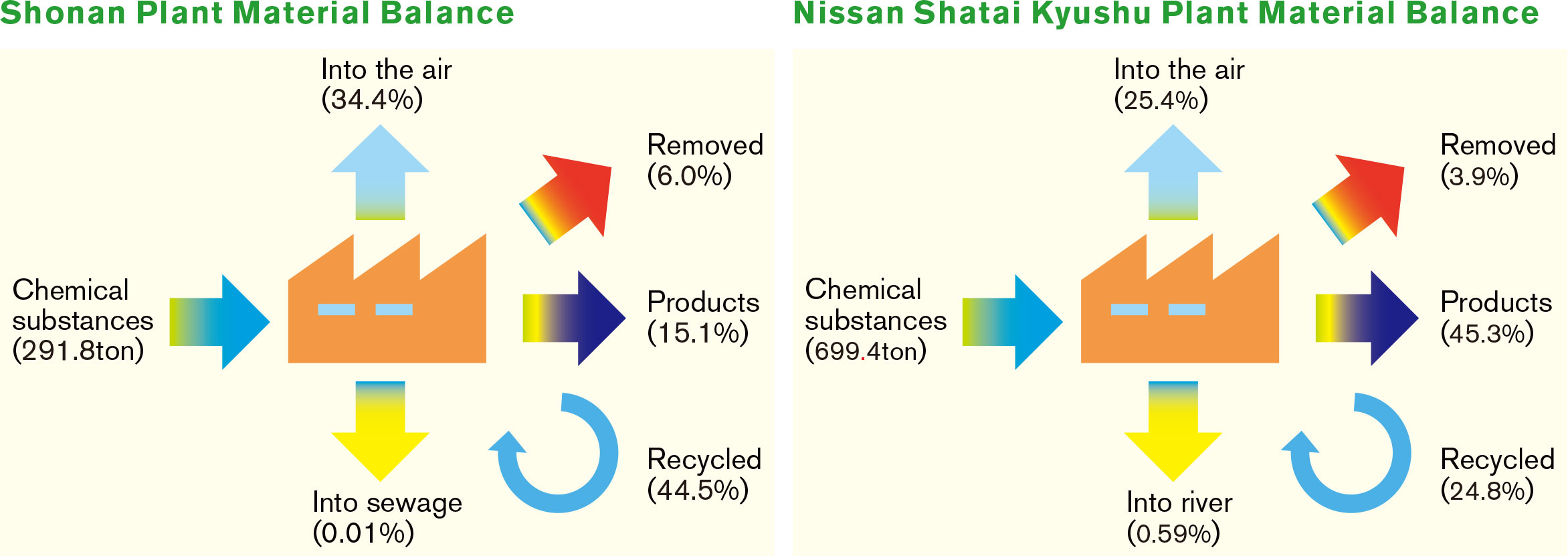
Reduction of Chemical Substances
The use of chemical substances has a close relationship to regional environmental conservation, so we are working to reduce the amount of chemical substances we use and release.
FY2024 Achievements
VOCs* account for more than 90% of the chemical substances released by Nissan Shatai.
Nissan Shatai has set the target of 43.1g/m2 or less and Nissan Shatai Kyushu has set the target of 28.2g/m2 or less and they achieved these targets in FY2024.
Nissan Shatai Kyushu has set a lower target value than Nissan Shatai by adopting water-based paint in a part of the painting process.
* VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds): the toluene, xylene, etc. used in paint solvents, etc.
Substances included in the PRTR*
Amounts of substances included in the PRTR released and transferred in FY2024
Data aggregation period: April 1, 2024 to March 31, 2025
Unit: kg/year
| Release and transfer destination | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Sub- stance number |
Name of sub- stance |
Handled quantity |
Releases to the air |
Releases to water areas (sewers) |
Tran- sfer as waste |
In- house land- fill |
Recycled | Chemical change |
Product consum- ption amount |
| [Head office and Shonan Plant] | ||||||||||
| Spe- cific 1 |
400 | Benzene | 987 | 1 | 986 | |||||
| 1 | 1 | Water- soluble compounds of zinc |
1,745 | 12 | 40 | 1,693 | ||||
| 1 | 53 | Ethyl- benzene |
90,909 | 30,385 | 9 | 56,522 | 3,990 | 3 | ||
| 1 | 80 | Xylene | 78,453 | 27,621 | 9 | 40,456 | 4,289 | 6,078 | ||
| 1 | 300 | Toluene | 64,883 | 27,009 | 2 | 18,938 | 5,570 | 13,364 | ||
| 1 | 302 | Naphtha lene |
1,130 | 725 | 34 | 371 | ||||
| 1 | 392 | Hexane | 5,778 | 20 | 5,758 | |||||
| 1 | 594 | Ethylene Glycol Monobutyl Ether |
37,188 | 17,749 | 5 | 13,788 | 5,646 | |||
| 1 | 627 | Diethylene Glycol Monobutyl Ether |
1,784 | 1,680 | 54 | 50 | ||||
| 1 | 629 | Cyclo hexane |
3,500 | 2,400 | 105 | 995 | ||||
| 1 | 691 | trimethyl- benzene |
20,296 | 8,910 | 3,225 | 1,477 | 6,684 | |||
| 1 | 720 | 2- tert- Butoxy ethanol |
3,617 | 719 | 2,897 | 1 | ||||
| 1 | 737 | Methyl isobutyl ketone |
2,004 | 778 | 1,176 | 50 | ||||
| Total | 311,287 | 117,997 | 12 | 65 | 0 | 137,195 | 22,439 | 34,566 | ||
| [Hadano area] | ||||||||||
| 1 | 80 | Xylene | 1,600 | 6 | 1,594 | |||||
| 1 | 300 | Toluene | 1,607 | 3 | 1,604 | |||||
| 1 | 691 | trimethyl- benzene |
2,397 | 18 | 1 | 2,378 | ||||
| Total | 5,604 | 27 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5,576 | ||
| [Techno Center] | ||||||||||
| 1 | 300 | Toluene | 1,033 | 233 | 12 | 36 | 1 | 752 | ||
| Total | 1,033 | 233 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 36 | 1 | 752 | ||
| [Nissan Shatai Kyushu] | ||||||||||
| Spe- cific 1 |
309 | Nickel compound |
2,436 | 10 | 1,549 | 49 | 828 | |||
| Spe- cific 1 |
400 | Benzene | 4,326 | 5 | 4,321 | |||||
| 1 | 1 | Water- soluble compounds of zinc |
14,222 | 43 | 1,806 | 12,373 | ||||
| 1 | 53 | Ethyl- benzene |
130,313 | 14,346 | 51 | 102,932 | 2,415 | 10,569 | ||
| 1 | 80 | Xylene | 145,008 | 13,607 | 85 | 83,573 | 2,485 | 45,258 | ||
| 1 | 300 | Toluene | 202,190 | 17,759 | 35 | 34,470 | 2,738 | 147,188 | ||
| 1 | 392 | Hexane | 14,041 | 44 | 1 | 13,996 | ||||
| 1 | 412 | Manganese and its compounds |
4,169 | 1 | 8 | 1,514 | 67 | 2,579 | ||
| 1 | 594 | Ethylene Glycol Monobutyl Ether |
114,695 | 31,500 | 132 | 7,227 | 14,560 | 10,891 | 50,385 | |
| 1 | 627 | Diethylene Glycol Monobutyl Ether |
3,200 | 2,192 | 96 | 912 | ||||
| 1 | 629 | Cyclo hexane |
4,324 | 3,935 | 130 | 259 | ||||
| 1 | 691 | trimethyl- benzene |
1,034 | 465 | 22 | 240 | 307 | |||
| 1 | 720 | 2- tert- Butoxy ethanol |
28,798 | 2,016 | 26,782 | |||||
| 1 | 731 | Heptane | 9,356 | 5,900 | 1 | 277 | 3,042 | 136 | ||
| 1 | 737 | Methyl isobutyl ketone |
32,347 | 2,268 | 31 | 522 | 17,807 | 61 | 11,658 | |
| Total | 710,459 | 94,038 | 224 | 12,791 | 0 | 280,649 | 23,159 | 299,598 | ||
* PRTR (Pollutant Release and Transfer Register): Companies, etc. prepare an inventory of the amount of pollutants released into air and water and amount produced as waste (the transferred amount) for each type of pollutant, etc. and register the catalog with the government, etc. Doing this encourages the voluntary reduction of pollutants.
Mechanism for substance management
In the case that we wish to newly introduce raw materials, we judge whether or not they should be adopted by evaluating in advance the risks of the chemical substances to the environment and safety based on the New Raw Materials Management System.
Odor Prevention and Paint Mist Scattering Prevention
We are actively taking a variety of countermeasures based on our perception that it is necessary to minimize the impact on the neighborhood of the odor and paint mist which are mainly generated from the painting plant.
Content of the main initiatives
The sources of generation of odor and paint mist and our main initiatives are shown in the following diagram.
Painting booth exhaust odor countermeasures and paint mist scattering prevention
·Air freshener spray (exhaust odor)Nissan Shatai’s painting plant adjacent to a residential area has introduced an air freshener spray diffusing system as a countermeasure against odor caused by exhaust from the painting booth. We are also changing our air freshener to a more effective one. In 2019, we expanded the scope of the air freshener spraying to strengthen the prevention of diffusion of the odor.
·High performance filter (paint mist)fter we have carried out primary removal of the paint mist (fine particles) contained in the painting booth exhaust using wet exhaust cleaning equipment with a water shower, we carry out secondary removal with an even higher performance filter (with a particle diameter of 10μm and a filtration rate of 99.3%) to achieve clean exhaust.
Odor countermeasures
In order to ensure that solvent odor does not leak into the region from Nissan Shatai Shonan’s painting plant, in addition to the air freshener diffusion we have adopted previously, we have also installed plasma deodorization equipment to reduce the odor emitted from the exhaust ducts. Moreover, we commenced the introduction of odor reduction by installing activated charcoal filters on the exhaust routes.
·Agglomeration collection equipment (paint sludge collection system)The dirty water and paint residue inside the circulation water tank can easily decompose and emit bad smells of hydrogen sulfide, etc. Therefore, we are preventing decomposition by pumping in air using an aeration nozzle.
Furthermore, we use a pump to collect the paint sludge which is the origin of the odor, send the paint sludge to a thickening tank, and then remove its moisture content before sending it for recycling.
Drying oven exhaust odor countermeasures
·Deodorization equipmentCars painted in the painting booth are dried in drying ovens, but they have quite a strong thinner smell. We have installed deodorization equipment in all of the drying ovens, and currently we are using platinum catalyst type deodorization equipment or heat storage type deodorization equipment, depending on the application. The platinum catalyst type is air freshening equipment which breaks down the VOCs by heating them to about 350℃ and is effective for countermeasures against VOCs released from drying ovens.

Painting booth exhaust duct

High-performance filters
Countermeasures against paint mist from the painting process
Plasma deodorization equipment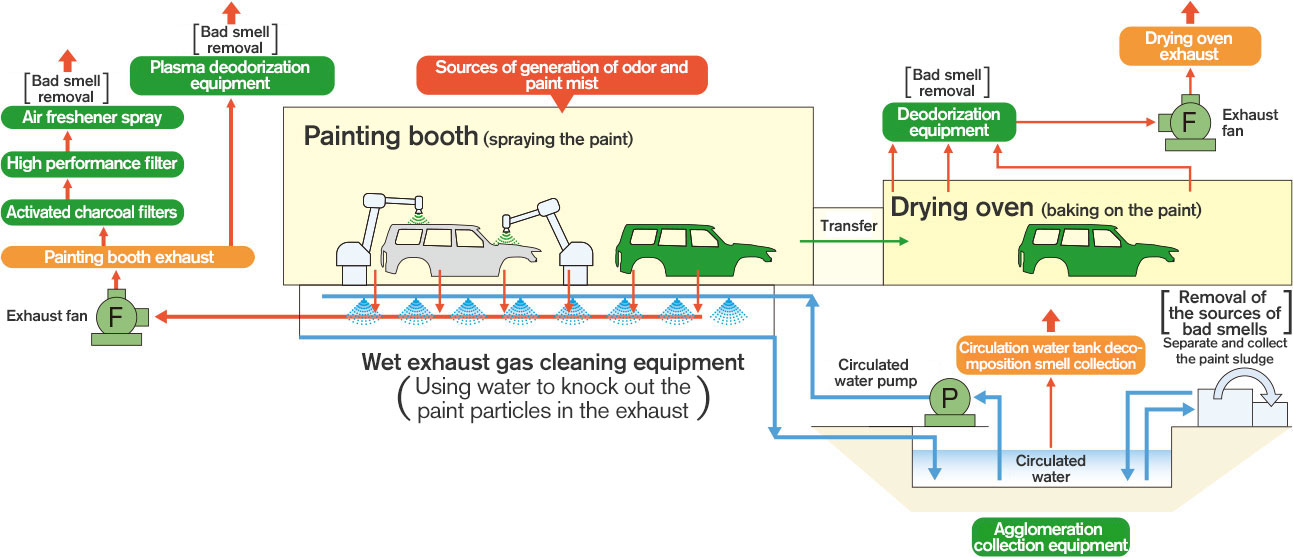
Effective Utilization of Water Resources
We are working on the protection of water resources to contribute to the objective of “enhance water risk management at manufacturing sites” in the Nissan Green Program. Nissan Shatai is also advancing activities in line with this objective.
Content of the main initiatives
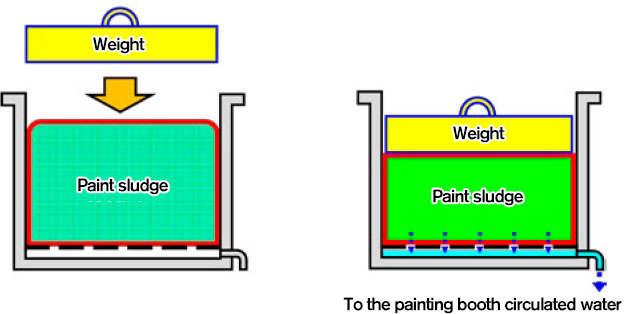
Introduction of the paint sludge collection system (agglomeration collection equipment)
This is a system which reduces the amount of water used by collecting the paint sludge mixed into the water circulating between the painting booth and the sedimentation tank to clean the circulated water and use it repeatedly.
This system is also useful for odor prevention.
There are a lot of moisture content still remains in the collected paint sludge.
We also use this moisture content as booth circulated water by placing a weight on it to squeeze it out as shown in the diagram below, and we are producing good results with respect to reduction in the amount of waste as well.

Paint sludge moisture content extraction equipment

Paint sludge moisture content extraction equipment

The initiatives of Nissan Shatai Kyushu
Nissan Shatai Kyushu has introduced state-of-the-art equipment incorporating the know-how cultivated at Nissan Shatai to tackle the effective utilization of water resources.
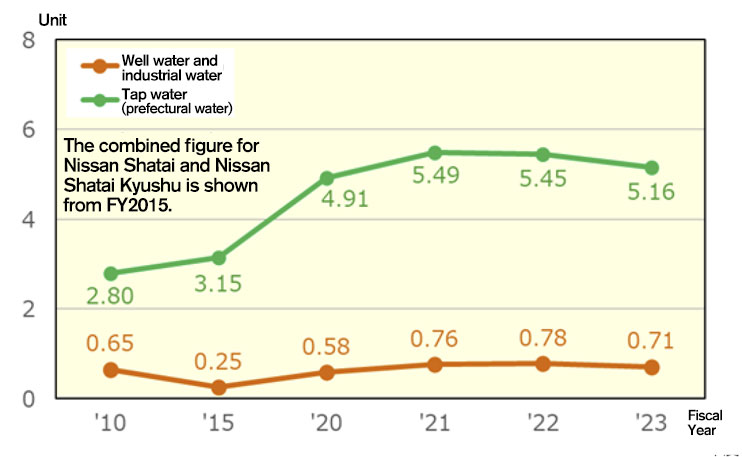
Management of the amount of water used
Among the vehicle production processes, water is particularly necessary in the painting process. Therefore, we are managing the amount of water used in order to protect water resources.
-
Trend in the amount of water used per vehicle

RO equipment
RO equipment: This is equipment which filters the impurities in raw water to refine it into highly pure water, using the reverse osmosis membrane which utilizes the water “osmosis” phenomenon in reverse (Reverse Osmosis). It can reduce the amount of raw water used for the refinement of water at the necessary purity.
Prevention of Water and Air Pollution
Nissan Shatai is in an environment blessed with nature including the sea, mountains, rivers and fields, so it has established voluntary standard values and is endeavoring to achieve environmental conservation stricter than laws and regulations in its management of air and water quality.
In particular in the Hadano region we are blessed by greenery and water, including the famous water springs of the Tanzawa Mountains, etc., so we always pay close attention to water quality management.
Nissan Shatai Kyushu has a plant facing the Seto Inland Sea and is also implementing strict water quality management together with Nissan Motor Kyushu Co., Ltd. which carries out its production inside the same site.
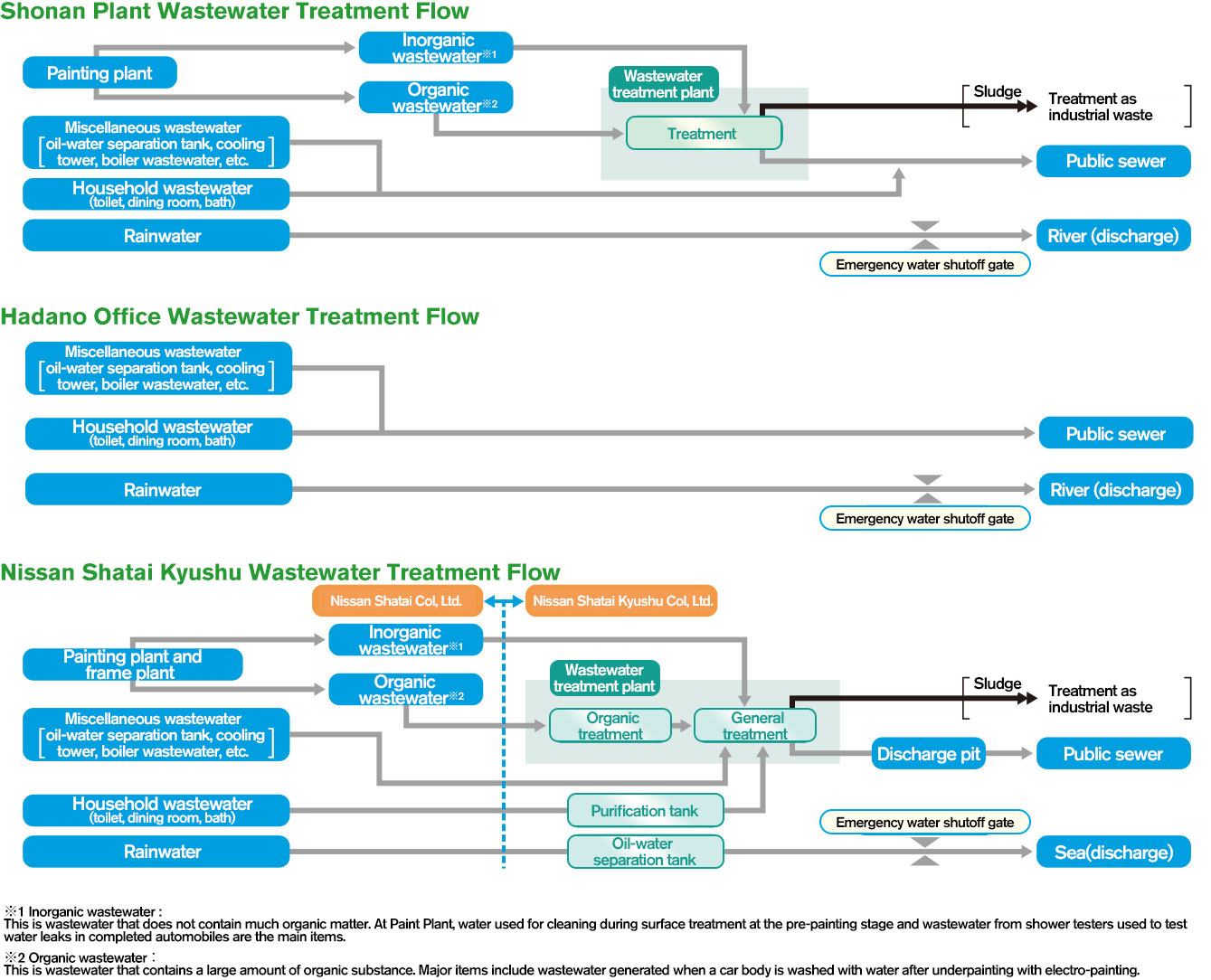
Prevention of water contamination
We treat the wastewater from the plants appropriately at a wastewater treatment plant and then discharge it into public sewers and rivers.
Prevention of air pollution
Reduction of sulfur oxides (SOx) and nitrogen oxides (NOx)
The Shonan Plant uses city gas to greatly reduce SOx. Furthermore, it is also reducing NOx by adopting quality fuels such as city gas, etc., implementing combustion management, and using denitration equipment which reduces the NOx concentration in exhaust gas, etc.
Reduction of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Nissan Shatai has a painting process, so it has already been tackling the reduction of VOCs for some time. Going forward, it will work on further improvements.
Nissan Shatai Kyushu has adopted water-based paint in the topcoat color base and has reduced VOC emissions per unit by 28% compared to the Shonan Plant.Moreover, since FY2021 it has worked on adopting water-based paint for the middle coat paint and it completed the switch for all colors in June 2023. Compared to before the switch, it has reduced VOC emissions by 39%.
Prevention of the contamination of soil and groundwater
Believing that environment impact inspections of soil and groundwater are important for environmental conservation, we are voluntarily implementing studies on our history of use of the chemical substances we have used in the past, and also soil and groundwater inspections.
Inspections of Contamination and Our Response
| Plant name | Circumstances of the inspection (when the inspections were completed) |
Pollutant | Status of response |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kyoto Plant |
Inspection when the plant was closed (2000 to 2001) |
There was benzene and arsenic soil contamination, but there was no contamination in the groundwater. |
oil purification completed (March 2002) |
| Zone 3 |
Inspections carried out when the previous owner closed the plant as a consequence of a land purchase (2000 to 2001) |
There was hexavalent chromium and fluorine soil contamination, but there was no contamination in the groundwater. |
Soil replacement completed (May 2002) |
| There was tetrachloroethylene soil and groundwater contamination. However, there was no outflow from the site boundary and the contamination was limited to inside the site. | Currently we are implementing soil and groundwater purification and monitoring. There is no contamination outflow from the site boundary. | ||
| Zone 2 |
Voluntary inspection (2001 to 2004) |
There was lead soil contamination in a tiny part of the surface layer, but there was no contamination in the groundwater. | This area is covered with concrete, so there is no concern regarding the scattering of contaminated earth. Furthermore, there is no concern regarding groundwater contamination, but we are continuing the monitoring of the groundwater just in case. |
| Zone 1 |
Inspection when the plant (2013) |
Among the 1,379 locations inspected, soil contamination was confirmed involving tetrachloroethylene, trichloroethylene, and benzene in one location each, lead in 33 locations, boron and hexavalent chromium in one location each, fluorine in five locations, and cyanogen in 17 locations, and in groundwater tetrachloroethylene was detected in six locations, benzene in one location, and cyanogen in two locations, and it was confirmed that each of these substances exceeded the designated standards of the Soil Contamination Countermeasures Act. | We have treated each of these locations in accordance with the measures and methods stipulated under the Soil Contamination Countermeasures Act . |
In November 2012, Nissan Shatai conducted a soil inspection of the area of Zone 1 of Shonan Plant scheduled to be sold in accordance with the Soil Contamination Countermeasures Act and the Kanagawa Prefectural Ordinance on the Conservation of the Living Environment and reported the results of the inspection to Hiratsuka City in December 2013.
Consequently, Hiratsuka City designated it as an “area which requires action” and “an area for which notification is required upon change to form or nature,” and from March 2014, Nissan Shatai launched a soil improvement project based on the Soil Contamination Countermeasures Act. It has now completed the project and sold the area.
Management going forward
We are mapping and managing the history of our past use of the harmful substances which are a factor behind soil contamination.
Before implementing land excavation, we implement soil contamination inspections based on that use history map to prevent in advance the removal of the contaminated soil from the site.
Purchasing of Environmentally-Friendly Products
Purchasing of environmentally-friendly parts is important for making environmentally-friendly vehicles. We are implementing “green purchasing” which involves giving priority to the purchasing of products (parts and materials) with a small impact on the environment from environmentally-friendly suppliers.
Implementation of green purchasing
We provide vehicles to our customers, products comprised of tens of thousands of parts, and we are working with the suppliers who deliver those parts on the green purchasing of environmentally-friendly parts and materials with little impact on the environment. The following three items are our purchasing concepts.
i) Parts and materials with a small environmental impact
ii) A parts manufacturing process with a small environmental impact
iii) Suppliers with high environmental awareness
Reporting of environment-impacting substances data
We ask our suppliers to ensure that the delivered parts and materials conform with the “environment-impacting substances management standard” based on Nissan Motor’s own technical standards. At the development stage, we receive reports of environment-impacting substances data, such as the presence or absence of prohibited substances, the amount of caution-required substances used, etc. We use these reports to ascertain the status of the environmental impact at an early stage, avoid environmental risks, and develop alternative technologies.
Reporting of environment-impacting substances data
In order to ensure that the environmental management systems are robust, we are encouraging our suppliers to construct, maintain the operation of, upgrade, and update their own environmental management systems with “ISO14001 or equivalent external accreditation acquisition.”
Notification of the Environmental Management Administrators
In order to promote green purchasing activities by our suppliers and to strengthen their collaboration with Nissan Shatai, we get our suppliers to appoint an Environmental Management Administrator. Through those Environmental Management Administrators, Nissan Shatai provides information to the suppliers about our environmental activities and the environment impact of our products.